[Node分享] 事件循环在libuv中的实现
Viewed: loading...
18 minutes to read
libuv简介
概述
官网上摘了一段话: libuv is a multi-platform support library with a focus on asynchronous I/O. It was primarily developed for use by Node.js, but it’s also used by Luvit, Julia, pyuv, and others. libuv是一个专注于支持异步I/O的跨平台支持库。它主要是为Node.js开发的,但Luvit、Julia、pyuv和其他库也使用它。
概括来说:
- 它是由C语言编写的工具库
- 跨平台支持异步I / O模型
- 相对小的体积 ~ 30,000行 / 30K (不包括测试代码)
- 除Node.js也支持了其他语言
迭代过程
- Node.js最初使用libev支持事件循环
- libev依赖只支持UNIXes的kqueue or (e)poll
- libuv 做了层抽象
- UNIX: libev
- Windows: IOCP
- libev(event loop) + libio(thread pool) 开发出了 libuv
支持特性
- Event Loop
- TCP/UDP sockets
- Filesystem operations
- Child process
- Signal handling
- …
事件循环详解
开发中遇到的问题
- setTimeout它准吗
- setImmediate(fn) 和 setTimeout(fn)谁先输出呢
流程图
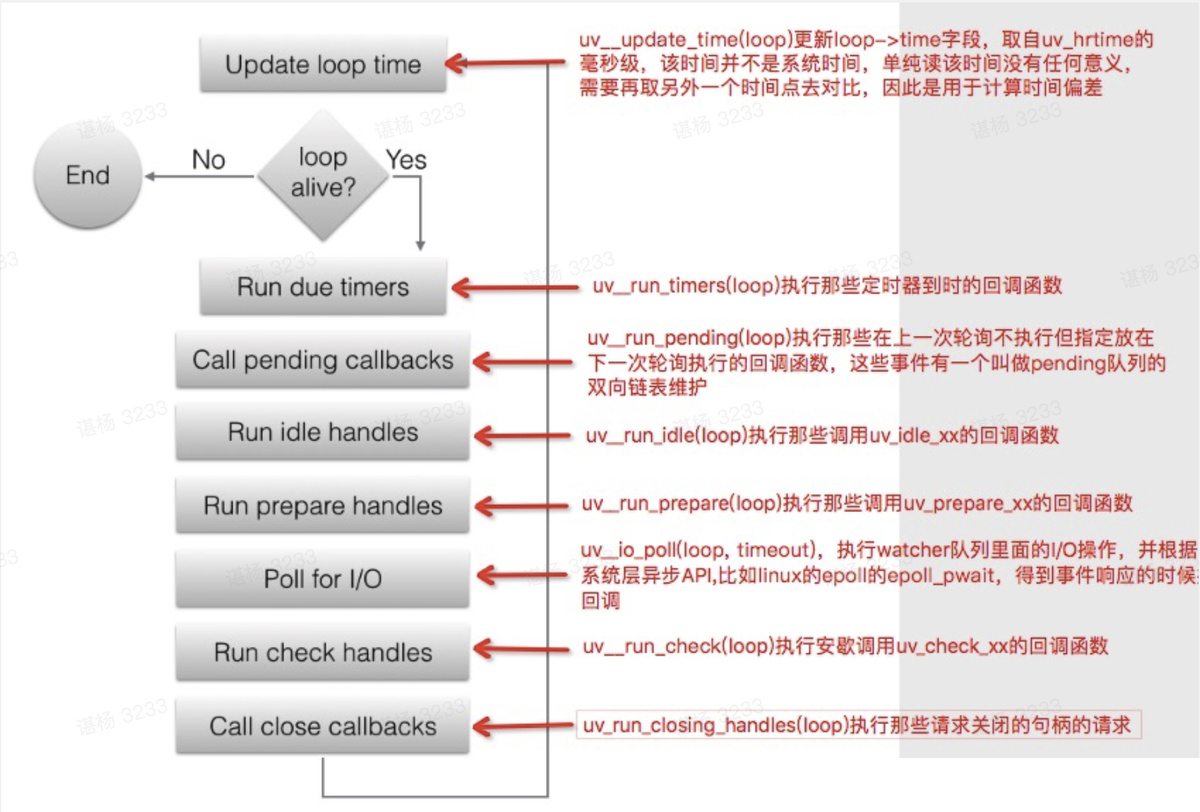
简要来说: 处理到期timers的回调 => 处理 I/O 回调 => idle/prepare(内部函数,可以不关注)=> 等等有没有处理完毕的事件 => check (内部函数,此时执行setImmediate) => 关闭handle并调用对应的回调函数
上述的流程,是在核心函数uv_run里实现的,我们来仔细看看这个函数
核心函数uv_run概览
// libuv/src/unix/core.c
int uv_run(uv_loop_t* loop, uv_run_mode mode) {
int timeout;
int r;
int ran_pending;
// 检查loop是否alive
r = uv__loop_alive(loop);
if (!r)
// 0. 更新time
uv__update_time(loop);
while (r != 0 && loop->stop_flag == 0) {
uv__update_time(loop);
// 1. 处理timer回调
uv__run_timers(loop);
// 2. 处理异步任务回调
ran_pending = uv__run_pending(loop);
// 3. 系统内部函数
uv__run_idle(loop);
uv__run_prepare(loop);
// 检查timeout,并验证是否跳过poll阶段
timeout = 0;
if ((mode == UV_RUN_ONCE && !ran_pending) || mode == UV_RUN_DEFAULT)
timeout = uv_backend_timeout(loop);
// 4. i/o poll
uv__io_poll(loop, timeout);
// 5. 执行setImmediate
uv__run_check(loop);
// 6. 关闭文件描述符等操作
uv__run_closing_handles(loop);
// 判断是否为UV_RUN_ONCE模式
if (mode == UV_RUN_ONCE) {
/* UV_RUN_ONCE implies forward progress: at least one callback must have
* been invoked when it returns. uv__io_poll() can return without doing
* I/O (meaning: no callbacks) when its timeout expires - which means we
* have pending timers that satisfy the forward progress constraint.
*
* UV_RUN_NOWAIT makes no guarantees about progress so it's omitted from
* the check.
*/
uv__update_time(loop);
uv__run_timers(loop);
}
// 再次检查循环是否活着
// 如果没有任何任务了,就退出
r = uv__loop_alive(loop);
if (mode == UV_RUN_ONCE || mode == UV_RUN_NOWAIT)
break;
// 再来一次
}
/* The if statement lets gcc compile it to a conditional store. Avoids
* dirtying a cache line.
*/
if (loop->stop_flag != 0)
loop->stop_flag = 0;
return r;
}各阶段详解
uv__loop_alive
// libuv/src/win/core.c
// libuv/src/unix/core.c
static int uv__loop_alive(const uv_loop_t* loop) {
return uv__has_active_handles(loop) ||
uv__has_active_reqs(loop) ||
loop->closing_handles != NULL; // unix
// loop->endgame_handles != NULL; (win)
}这里面做了三类判断:
- 循环结构体(uv_loop_t)中是否还存在活跃句柄(loop->active_handles)
- 是否存在请求句柄(loop->active_reqs.count)
- 其次,对未结束的句柄进行了判断
如果存在未结束的句柄,libuv则会在后面的uv__run_closing_handles(loop)函数内做一些额外工作:
- 进行句柄的unref操作
- 调用handle->close_cb(handle) 来触发执行close事件回调
uv__update_time
// libuv/unix/internal.h
UV_UNUSED(static void uv__update_time(uv_loop_t* loop)) {
/* Use a fast time source if available. We only need millisecond precision.
*/
loop->time = uv__hrtime(UV_CLOCK_FAST) / 1000000;
}这个loop->time则是event-loop中用来执行定时任务的时间计算器,每次调用他都会更新出最新的event-loop时间,这个时间会在后面决定是否进行io_poll轮询
它保存在libuv的uv_loop_t结构体中的time属性里
uv__run_timers
// libuv/src/timer.c
void uv__run_timers(uv_loop_t* loop) {
struct heap_node* heap_node;
uv_timer_t* handle;
for (;;) {
heap_node = heap_min(timer_heap(loop));
if (heap_node == NULL)
break;
handle = container_of(heap_node, uv_timer_t, heap_node);
if (handle->timeout > loop->time)
break;
// 将heap_node从timer_heap中中删除 并 active_handles--
uv_timer_stop(handle);
// 如果设置了repeat的话,重新插入最小堆
uv_timer_again(handle);
// 执行定时任务
handle->timer_cb(handle);
}
}timer 是按超时时间 timeout 存放在最小堆中的,这样,最小的的堆顶就是 timeout 最小的那个 timer,也就是最先到达超时时间的那个定时任务
所以在检查到期的定时任务时,只需要不断的获取堆顶的元素,并与当前时间比对即可:
- 如果没有堆顶元素,则没有任何定时器存在,函数将直接返回
- 如果当前时间小于定时任务的超时间,那么堆顶 timer 未到到超时时间,非堆顶的 timer 更没有达到超时时间,整个 uv__run_timers 也就会退出
- 如果当前时间大于或等于定时任务的超时间,这个 timer 就是一定达到或超过执行时间的。这时,就可以从 timer 堆中将其取出,然后调用其回调函数handle->timer_cb(handle)处理定时任务,然后再次重复获取下一个出现在堆顶的 timer,直到情况 1 或 2 成立
以下有两个主要注意的点:
- 大于或等于实际上包含两种情形:
- 如果当前时间等于定时任务的超时时间,就是最理想的状态了,因为定时任务会在定时器到来的时候准时被执行,与预期相符合
- 如果当前时间大于定时任务的超时时间,则是非理想的状态了,然而这种情形缺是最长出现的,因为很难保证当 timer 的超时时间到来时,程序刚好执行到此
- 如果定时任务的回调函数handle->timer_cb执行时间过长,将会导致整个循环阻塞在此处,从而影响其他定时器的处理,进而也影响到整个时间循环的其他逻辑的处理,因为只有一个线程在处理各类型的回调任务。
uv__run_pending
// libuv/src/core.c
static int uv__run_pending(uv_loop_t* loop) {
QUEUE* q;
QUEUE pq;
uv__io_t* w;
if (QUEUE_EMPTY(&loop->pending_queue))
return 0;
// 把该类型对应的队列中所有节点摘下来,挂载到queue变量
QUEUE_MOVE(&loop->pending_queue, &pq);
// 遍历 loop->pending_queue 队列
while (!QUEUE_EMPTY(&pq)) {
q = QUEUE_HEAD(&pq);
QUEUE_REMOVE(q);
QUEUE_INIT(q); // 断开队列连接
w = QUEUE_DATA(q, uv__io_t, pending_queue);
w->cb(loop, w, POLLOUT);
}
return 1;
}如果 pending_queue 为空,此函数将返回0。否则,该函数将遍历 loop->pending_queue 队列节点,取得 I/O 观察者后调用 cb,函数将返回1
uv_backend_timeout
// libuv/src/core.c
int uv_backend_timeout(const uv_loop_t* loop) {
// 这个标记是 0的时候,意味着事件循环跑完这一轮就退出了,返回的时间是0
if (loop->stop_flag != 0)
return 0;
// 如果没有任何的异步任务(包括timer和异步I/O),那timeout时间一定就是0了
if (!uv__has_active_handles(loop) && !uv__has_active_reqs(loop))
return 0;
// idle不为空的时候
if (!QUEUE_EMPTY(&loop->idle_handles))
return 0;
// pending_queue不为空的时候(uv__io_init会初始化pending_queue)
if (!QUEUE_EMPTY(&loop->pending_queue))
return 0;
// 我们的循环进入了关闭阶段,没必要等待了
if (loop->closing_handles)
return 0;
return uv__next_timeout(loop);
}见文中注释
接下来,进入到uv__next_timeout的源码
uv__next_timeout
// libuv/src/timer.c
int uv__next_timeout(const uv_loop_t* loop) {
const struct heap_node* heap_node;
const uv_timer_t* handle;
uint64_t diff;
// 获取最接近timout的node
heap_node = heap_min(timer_heap(loop));
if (heap_node == NULL)
return -1; /* block indefinitely */
// 获取handle->timtout
handle = container_of(heap_node, uv_timer_t, heap_node);
// 如果已经执行完了,则返回0
if (handle->timeout <= loop->time)
return 0;
// 否则获取到距离此时此刻,loop中,最先到期的一个timer的时间
diff = handle->timeout - loop->time;
// 不能大于最大的INT_MAX
if (diff > INT_MAX)
diff = INT_MAX;
return (int) diff;
}uv__io_poll
uv__io_poll的源码比较长,就不贴了主要功能就是轮询io执行情况,这个过程是阻塞的。
uv__io_poll从 uv__next_timeout 获得了一个最多是2147483647的一个等待时间,时间表示距离下一个timer需要执行(超过了timer的timeout)的时间
我们发现,原来libuv的事件循环也会阻塞
但其实只要有任务需要马上执行的时候,这个函数是不会被调用的。那么被调用的时候则是:所有被注册的异步任务都没有完成(返回)的时候。这时候等一下其实没什么所谓,等的就是这些异步任务会不会在这么极其短暂的时间内发生I/O完毕
那难道它会阻塞等待30min吗
也不是,这个timeout会使用update_timeout函数根据进入loop的事件来更新自己的值,update_timeout的代码如下:
assert(timeout > 0);
real_timeout -= (loop->time - base);
if (real_timeout <= 0)
return;
timeout = real_timeout;uv__run_closing_handles
// libuv/src/core.c
static void uv__run_closing_handles(uv_loop_t* loop) {
uv_handle_t* p;
uv_handle_t* q;
// unref
p = loop->closing_handles;
loop->closing_handles = NULL;
// 遍历handles,逐一关闭
while (p) {
q = p->next_closing;
uv__finish_close(p); // 此处触执行close事件回调
p = q;
}
}关闭所有的handles,触发close事件回调
uv_run_mode 简介
在介绍各个阶段之前,先详细介绍一下uv_run_mode,其取值有三种,分别为:
- UV_RUN_DEFAULT 默认轮询模式,此模式会一直运行事件循环直到没有活跃句柄、引用句柄、和请求句柄
- UV_RUN_ONCE 一次轮询模式
- 如果pending_queue中有回调,则会执行回调而直接跨过uv__io_poll
- 如果没有,则此方式会阻塞,执行一次i/o轮询(uv__io_poll)
- 如果在执行过后有回调压入到了pending_queue中,则uv_run会返回非0,需要在未来的某个时间再次触发一次uv_run来清空pending_queue
- UV_RUN_NOWAIT 一次轮询(无视pending_queue)模式,此模式类似UV_RUN_ONCE但是不会判断pending_queue是否存在回调,直接进行一次i/o轮询
DEMO
DEMO in Node.js
setTimeout 和 setImmeditate
在nodejs中,如果你输入如下代码:
setTimeout(()=>console.log(0));
setImmediate(()=>console.log(1));
// 1 0
// 0 1会发现输出顺序是随机的,接下来给大家详细解释一下这里的随机性,视线首先转移到setTimeout的实现原理[internal/timers.js]中:
function Timeout(callback, after, args, isRepeat) {
after *= 1; // coalesce to number or NaN
if (!(after >= 1 && after <= TIMEOUT_MAX)) {
// ...
after = 1; // schedule on next tick, follows browser behavior
}
// ...
}在这里对setTimeout的延迟时间做了判定,如果没有设定延迟时间则会默认为1毫秒的延迟触发
继而延伸到libuv,在event-loop的uv__run_timers中调用handle->timer_cb(handle)来触发回调
setImmediate是在uv__run_check阶段触发,在libuv进行初始化的过程中,如果时间小于1毫秒,则会直接跳过uv__run_timers使得uv__run_check中的回调队列优先触发;而如果初始化时间大于1毫秒,则会进入到uv__run_timers阶段优先触发setTimeout中的回调
但是如果在IO回调里,则永远是immediate先
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile(__filename, () => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(0);
}, 0);
setImmediate(() => {
console.log(1);
});
});
// 1 0由于timeout和immediate的事件注册是在readFile的回调执行时触发的,所以必然的,在readFile的回调执行前的每一次event loop进来的uv_run_timer都不会有超时事件触发
那么当readFile执行完毕,poll阶段收到监听的fd事件完成后,执行了该回调,此时
- timeout事件注册
- immediate事件注册
- 由于readFile的回调执行完毕,那么就会从uv_io_poll中出来,此时立即执行uv_run_check,所以immediate事件被执行掉
- 最后的uv_run_timer检查timeout事件,执行timeout事件
所以你会发现,在I/O回调中注册的两者,永远都是immediately先执行
